In today's digital age, the ability to process payments online is essential for businesses of all sizes. Whether you're running an e-commerce store, offering services online, or managing subscriptions, a payment gateway is a crucial component of your business's financial infrastructure. But what exactly is a payment gateway, and why is it so important?
Payment gateways act as the bridge between your cool business and the financial institutions that process customer payments. Understanding how these systems work can help you choose the right solution for your needs, ensuring smooth transactions, enhanced security, and a better overall customer experience. For any business looking to thrive in the online marketplace, a solid grasp of payment gateways is not just beneficial—it's essential.
Role of Payment Gateway in Online Transactions
A payment gateway plays a nice pivotal role in online transactions by acting as the intermediary between a customer's payment method and the merchant's bank account. When a customer makes a purchase, the payment gateway securely captures and encrypts the payment details, transmits them to the acquiring bank for authorization, and then relays the transaction approval or denial back to the merchant's website. This process, which typically takes just a few seconds, ensures that the payment is cool processed accurately and efficiently, allowing businesses to accept payments from customers across the globe.
In addition to streamlining transactions, payment gateways are critical for ensuring the security of online payments. According to a 2023 report by Statista, Payment gateways use advanced encryption protocols, such as SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and tokenization, to protect sensitive customer information from unauthorized access. They also comply with industry standards like PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard) to mitigate the risk of fraud and ensure that customers' payment data is handled securely. This security layer is essential for building trust with customers and protecting businesses from potential financial and reputational losses due to data breaches.
-(34).png)
Key Components of Payment Gateways
Encryption and Tokenization
Encryption and tokenization are crucial security measures that protect customer data during transactions. Encryption converts payment information into secure code, preventing unauthorized access during transmission. Tokenization replaces sensitive data, like credit card numbers, with unique tokens that are useless to attackers. These technologies are vital for online payment security and often mandated by standards like PCI DSS.
Payment Processing and Authorization
Payment processing and authorization are the core functions of a payment gateway. When a transaction is initiated, the gateway processes the payment info and communicates with the acquiring bank for authorization. This involves validating the payment method, checking for funds, and ensuring security standards are met. Efficient processing is essential for a seamless customer experience, especially in e-commerce.
Security and Fraud Detection
Payment gateways use advanced security features, such as machine learning algorithms and real-time monitoring, to detect and prevent fraud. By analyzing transaction patterns, they can flag suspicious activity and stop fraud before it occurs. This protects businesses from financial losses and helps build customer trust.
Reporting and Transaction Management
Reporting and transaction management tools give businesses insights into their transactions, allowing them to monitor payment statuses, track sales, and generate reports for accounting. These tools also handle refunds, chargebacks, and disputes. Robust reporting capabilities are crucial for maintaining financial accuracy and making informed business decisions.
Understanding these components helps businesses make informed choices when selecting and integrating payment gateways, ensuring secure and efficient online transactions.
Payment Gateway Types
Hosted Payment Gateways
Hosted payment gateways redirect customers to a third-party payment processor's page to complete their transactions. This type of gateway handles the entire payment process, including data security and compliance with industry standards like PCI DSS. Hosted gateways, such as PayPal and Stripe, are popular among small to medium-sized businesses because they simplify integration and reduce the burden of maintaining security protocols. While they offer convenience and robust security, the downside is that customers are taken away from the merchant’s website during the payment process, which could potentially disrupt the user experience and affect conversion rates.
Integrated Payment Gateways
Integrated payment gateways, also known as non-hosted or on-site gateways, allow customers to complete transactions directly on the merchant’s website without being redirected to a third-party site. This seamless experience is beneficial for businesses looking to maintain brand consistency and improve user experience, as the entire transaction process is handled on their domain. Integrated gateways typically require more complex technical integration and higher security measures, as the business is responsible for securing customer data. However, the enhanced control and potential for a smoother checkout process make integrated payment gateways a preferred choice for larger businesses and ecommerce platforms.
Non-Hosted Payment Gateways
Non-hosted payment gateways process payments on the merchant's website but differ from integrated gateways in their implementation. They may rely on external resources for certain parts of the process, offering a balance between customization and convenience. While allowing businesses to control the checkout experience, non-hosted gateways can introduce integration complexities and may require more technical expertise.
Direct Post Payment Gateways
Direct post gateways let businesses collect payment information on their servers before posting it to the processor. This allows for a seamless checkout experience without redirecting customers to a third-party site. However, since payment data passes through the merchant's server, businesses must implement strong security measures to comply with PCI DSS. Direct post gateways offer high control and customization but require advanced technical capabilities and security infrastructure.
Comparison of Different Types of Payment Gateways
- Hosted Gateways: Ideal for small businesses prioritizing simplicity and security, but offer less control over the checkout experience.
- Integrated/Non-Hosted Gateways: Provide a branded checkout process and are better suited for larger businesses that can manage complex integrations and security.
- Direct Post Gateways: Offer maximum control and customization but require stringent security measures.
The choice depends on business size, technical capabilities, and the priority between user experience, security, and compliance. Understanding these options helps businesses select the best payment gateway for their needs.
How to Choose the Right Payment Gateway for Your Business
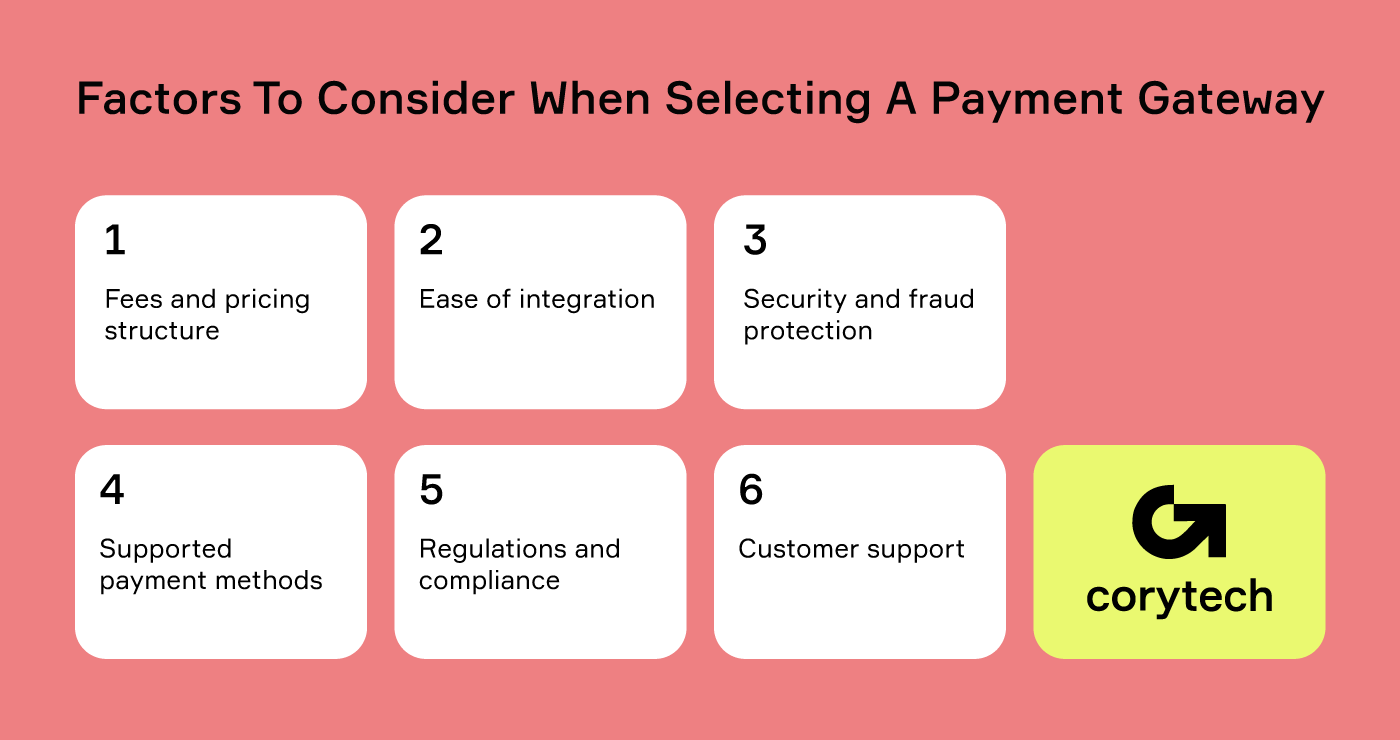
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Payment Gateway
Fees and Pricing Structure
Payment gateways charge various fees, including setup, monthly, and transaction fees, which can vary widely. For example, PayPal charges around 2.9% + $0.30 per transaction, while others might offer lower rates with additional monthly fees. Since transaction fees directly affect profit margins, especially for small businesses, it's crucial to understand the fee structure. A McKinsey & Company study found that 52% of businesses consider transaction fees the most important factor when choosing a gateway.
Ease of Integration
A straightforward integration process saves time and reduces technical issues. Many payment gateways offer developer documentation, pre-built plugins, and APIs for easy integration with platforms like Shopify, WooCommerce, or Magento. According to Statista, 38% of businesses view ease of integration as key when selecting a payment gateway. Choosing a gateway that integrates well with your systems can streamline operations and ensure a seamless checkout experience.
Security and Fraud Protection
Security is paramount when choosing a payment gateway. Robust measures like encryption, tokenization, and SSL technology are essential to protect customer data. Advanced fraud detection tools, such as machine learning and real-time monitoring, help prevent fraud. A 2023 Juniper Research report estimates online payment fraud losses will exceed $48 billion globally, highlighting the need for strong security features in your gateway.
Supported Payment Methods
A gateway should support various payment options, including credit/debit cards, digital wallets, and alternative methods like bank transfers or BNPL services. Offering multiple options can boost conversion rates; nearly 7% of shoppers abandon carts due to a lack of payment options, according to the Baymard Institute. Ensure the gateway supports the payment methods preferred by your target audience.
Regulations and Compliance
Compliance with regulations like PCI DSS and GDPR is critical to avoid legal issues and fines. PCI DSS mandates security measures to protect cardholder data, while GDPR governs personal data handling in the EU. Ensure your payment gateway complies with relevant regulations, including any specific to your industry or region.
Customer Support
Reliable customer support is crucial for resolving issues that could disrupt payment processing. Look for providers offering 24/7 support through various channels like phone, email, and live chat. Zendesk found that 67% of consumers consider good customer support essential for retention. A gateway with responsive support can help maintain smooth operations.
By evaluating these factors, businesses can choose a payment gateway that meets their needs and supports long-term growth in e-commerce.
Comparing popular payment gateways
|
Payment Gateway |
Transaction Fees |
Supported Payment Methods |
Ease of Integration |
Security and Fraud Protection |
Customer Support |
Compliance and Regulations |
|
|
1 |
2.9% + $0.30 |
Credit/Debit Cards, Digital Wallets (Apple Pay, Google Pay), Bank Transfers |
Highly customizable APIs, pre-built plugins |
Advanced encryption, fraud detection tools, PCI DSS compliant |
24/7 support via email, chat, and phone |
PCI DSS, GDPR compliant |
|
|
2 |
2.9% + $0.30 |
Credit/Debit Cards, Digital Wallets (Shop Pay, Apple Pay, Google Pay) |
Seamless with Shopify platform, limited with others |
Built-in fraud analysis, PCI DSS compliant, SSL encryption |
24/7 support via chat and email (phone support for higher plans) |
PCI DSS, GDPR compliant |
|
|
3 |
2.9% + $0.30 |
Credit/Debit Cards, eChecks, Digital Wallets |
Requires developer expertise, extensive API documentation |
Fraud detection suite, encryption, PCI DSS compliant |
24/7 support via phone, email, and live chat |
PCI DSS, GDPR compliant |
|
|
4 |
Varies (typically 0.1%) |
Cryptocurrencies (BTC, ETH, etc.), Credit/Debit Cards |
Moderate, API available for custom integration |
Two-factor authentication, cold storage for funds, encryption |
Email and ticket-based support, 24/7 chat for VIP users |
Complies with cryptocurrency regulations, KYC/AML policies |
|
|
5 |
1.49% |
Cryptocurrencies (BTC, ETH, etc.), Bank Transfers, Credit/Debit Cards |
Moderate, API available, Coinbase Commerce for easier integration |
Two-factor authentication, cold storage, PCI DSS compliant |
Email support, limited chat support, 24/7 for certain services |
Complies with cryptocurrency regulations, KYC/AML policies, PCI DSS |
![Welcome to API 3.0 and Corytech's New Merchant App!]() Written by Corytech Team
Welcome to API 3.0 and Corytech's New Merchant App!
We’re thrilled to introduce two major updates that are set to make your experience with Corytech even better: the transition to API 3.0 and improved Merchant App.
Written by Corytech Team
Welcome to API 3.0 and Corytech's New Merchant App!
We’re thrilled to introduce two major updates that are set to make your experience with Corytech even better: the transition to API 3.0 and improved Merchant App.
Integrating a Payment Gateway into an Existing Software Ecosystem
Common Steps for Integrating Payment Gateways
Integrating a payment gateway typically involves selecting a compatible provider, setting up a merchant account, and obtaining API keys or SDKs. You'll then embed payment forms into your website or app and configure the gateway settings. Many platforms, like Shopify, offer plugins to simplify this process. According to W3Techs, around 60% of e-commerce sites use such plugins for easier integration.
Tips for a Smooth Integration Process
For a smooth integration, start by thoroughly reviewing the gateway's documentation and using a sandbox environment for testing. Ensure the payment process is user-friendly to reduce cart abandonment, which affects 18% of online shoppers, according to the Baymard Institute. Early communication with your development team and the gateway's support can also prevent issues.
Testing and Troubleshooting
Testing in a sandbox environment is crucial to ensure all payment functions work correctly before going live. Focus on handling edge cases like failed payments and refunds. According to Forrester, thorough testing can reduce post-launch issues by 30%. Use the gateway's error reporting tools to resolve any issues quickly and keep your integration updated to maintain reliability.
Payment Gateways FAQ
What is a High-Risk Payment Gateway?
A high-risk payment gateway handles transactions for businesses considered high-risk due to factors like industry type or chargebacks. Examples include online gambling and adult entertainment. These gateways have higher fees and stricter security to mitigate fraud and chargebacks, essential for businesses struggling to get approval from standard processors.
What is Payment Gateway Integration?
Payment gateway integration connects a payment gateway to a website or app for processing transactions. It involves embedding the gateway's API or using plugins to create a seamless checkout. Proper integration is crucial for a smooth, secure payment process that enhances customer experience and supports growth.
What is an Acquiring Bank in a Payment Gateway?
An acquiring bank handles credit or debit card transactions via payment gateways on behalf of merchants. It receives transaction data from the gateway and passes it to the issuing bank for approval. When approved, it facilitates the transfer of funds to the merchant's account, ensuring businesses are paid for their goods and services.
What’s Next?
Choosing the right payment gateway is essential for optimizing your business's payment processes. With the correct setup, managing transactions, ensuring security, and providing a seamless customer experience can become much more manageable. Corytech offers an innovative, fully-featured platform that can help streamline your payment processing, regardless of your business size or industry.
Ready to take your payments to the next level? Request a personalized demo to see how Corytech can transform your payment experience.
.png)







 Payments
Payments
 Solutions
Solutions
 Industries
Industries
 Services
Services
 Resources
Resources

.png)










